In human research, significant advancement has been achieved with molecular biological tools. But for a better understanding of disease biology, an animal model like the mouse model is needed to have genetic similarities with humans.
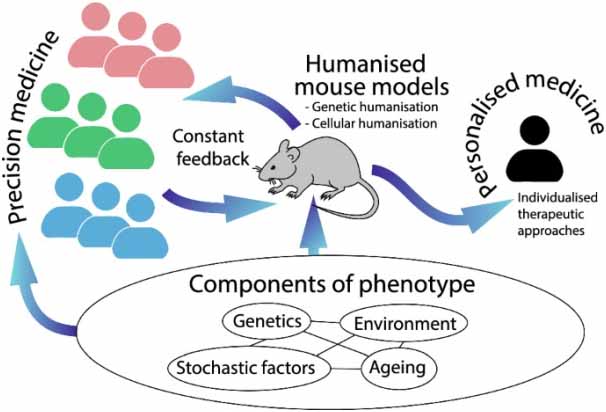 For preclinical studies, mouse models are commonly used gizmo to predict the disease outcome in humans. The role of the mouse model is significant due to being genetically similar (99%) to humans and successfully used for various aspects of human research, including genome-related diseases, immunological disorders, oncological conditions, pharmacological studies, and reproduction-related studies. To elaborate on the role of the mouse model, here are the reasons why mouse models are used in gene therapy research:
For preclinical studies, mouse models are commonly used gizmo to predict the disease outcome in humans. The role of the mouse model is significant due to being genetically similar (99%) to humans and successfully used for various aspects of human research, including genome-related diseases, immunological disorders, oncological conditions, pharmacological studies, and reproduction-related studies. To elaborate on the role of the mouse model, here are the reasons why mouse models are used in gene therapy research:
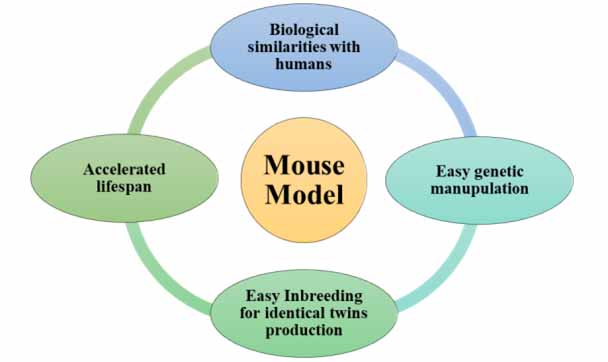
1. They are biologically similar to humans
The mouse has similarities with a human concerning genetics, anatomy, and physiology. For example, the laboratory mouse used for human studies has genetic similarities with wild-type mice. These are better than insects, and worms for exploring the complex biological systems of humans (skeletal, nervous, cardiovascular, endocrine, and immune) in similarity with human mice naturally acquire diseases associated with these systems. In addition, the immunologically incompetent mouse can be used for growing human tissues (healthy and diseased) that will be an important gizmo for cancer and AIDs research.
2. They can be manipulated to mimic human disease (condition)
The role of the mouse model is pivotal for studying pathology and control of complex diseases, i.e., hypertension, atherosclerosis, genetic disorders, and immunological disorders. The use of mice helps to look deep into genetic involvement in diseases. The mouse can be easily manipulated (insertion and deletion of the gene are easy and better) compared to other animals. Such characteristics help in exploring genetic diseases.
3. They can be inbred to yield genetically identical strains
The mouse model has high reproductive performance with a short generation time and larger litter size. Various genetically identical strains can be manufactured via inbreeding with special reference to increase their number and explore inbreeding-related disorders.
4. They share an accelerated lifespan
The role of the mouse model is significant due to its overall extended lifespan of 12-18 months with a very short generation time of 10 weeks and a gestation length of 21 days. Mouse colonies can be abducted very easily within a short period.
How Are Mouse Models Used in Gene Therapy Research?
Gene-related diseases are emerging in humans, and it is difficult to study these genetic conditions in humans. Mouse genetic makeup is more than 90% like humans, so these can be used in the placement of humans for genetic disorders. The gene insertion and deletion can be performed easily in the mouse. Below are the advantages of mouse models in gene therapy search:
1. Cost-effective and efficient research tool
The role of the mouse model is vital as cost-effective laboratory animals (cheaper and easier to look after) for human studies. The reproductive efficiency of mice is very high as they reproduce their offspring after every three weeks. Further, they have a large litter size, and therefore lots of mice are available easily for research purposes. Most laboratory mice are small, docile, and convenient to be kept easily. The generation time from birth to production of their offspring after getting adults is very short, which is mainly about 10 weeks. So, various generations can be observed in a short time, and aging effects can be observed as well.
2. Provide more accurate and useful disease research data
The role of mouse model invalidation of drug targets and effective dose determination allow the augmented use of mouse models in human research. These mouse models can be easily generated and maintained in laboratories. Genetically modified mouse reproduces shortly and is cost-effective and robust to be included as an optimal candidate for pharmacological research. The phenotypic characteristics of genetically modified mice can be validated easily, and such properties can be used to explore gene functionality. Useful data is obtained from mice following their application in human-related research.
3. Strong relevancy
Genetically, the mouse model is identical to the human genome (90%) with few exceptions. Human disease pathobiology and responses can be explored in a mouse model with similar results as in humans.
Cyagen custom mouse model is effective, easily available, cost-effective, and genetically similar to humans. Choose the Cyagen for your research to get good quality results in limited time duration.







